DataEncryptionStandard(DES)isawidelyuseddataencryptionmethodthatusesakey.TheUSgovernmentbelievesthatthekeyisdifficulttocrackandrestrictsitsexporttoothercountries.Thereare72petaflopsormoreencryptionkeysavailable.Foreachspecificpieceofinformation,itskeyisrandomlysampledfromahugenumberofkeylibraries.Likeotherprivatekeyencryptionmethods,thesenderandreceivermustknowandusethesamekey.
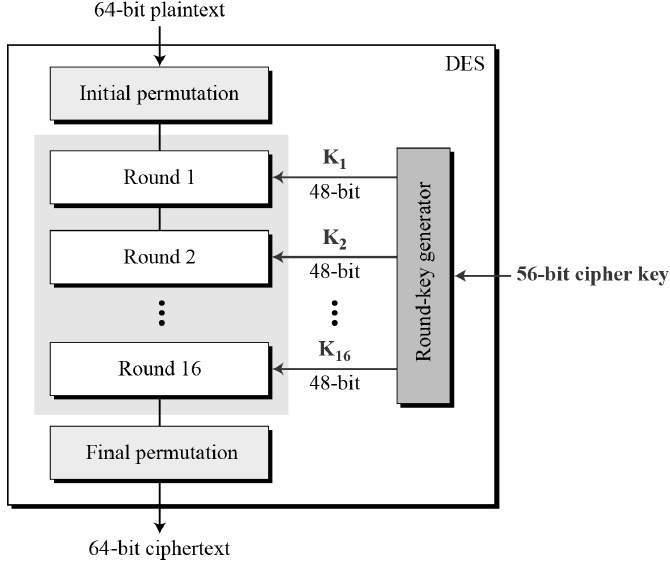
TheDigitalEncryptionStandard(DES)usesa56-bitkeyforeach64-bitdatablock.Theencryptionprocesscanbeoperatedinseveralmodesincluding16cyclesoroperations.Althoughitisconsidered"strong"encryption,manycompaniesusethreekeys,the"TripleDigitalEncryptionStandard(DES)".ThisisnottosaythatDESencryptedinformationcannotbecracked.Asearlyas1997,theownerofanotherencryptionmethodpublickeyencryptionalgorithm(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)offeredarewardof$10,000tocrackdigitalencryptionstandardinformation.Morethan14,000computerusersworkedtogetherthroughtheInternet.Theytriedvariouskeys,andfinallyfoundthatthekeyhaddecipheredtheinformationbyrunning18quadrillionkeys.Thedigitalencryptionstandardinformationisunlikelytobedecryptedonthisscale.
In1977,IBMcreatedadigitalencryptionstandard,whichwaslateradoptedbytheUSDepartmentofDefense.ItisspecifiedbytheAmericanNationalStandardsInstitute(ANSI)X3.92andX3.106standardsandtheFederalInformationProcessingStandard(FIPS)46and81standards.Consideringthatencryptionalgorithmsmaybeusedbyunfriendlygovernments,theUSgovernmenthasbannedtheexportofencryptionsoftware.However,thefreeversionofthesoftwareiswidelyavailablefromelectronicbulletinboardservicesandwebsites.Becausetheencryptionalgorithmisstillrelativelyunbreakable,theNationalInstituteofStandardsandTechnology(NIST)statedthatasastandard,theDigitalEncryptionStandard(DES)willnotbere-verified.ThenextstandardwillbecalledtheAdvancedEncryptionStandard(AES).
