Introduction
DevelopmentStatus
GigabitEthernetisatechnologybasedonbasicEthernetstandards.GigabitEthernetandthewidelyusedEthernetarefullycompatiblewithFastEthernet,anduseallthetechnicalspecificationsstipulatedbytheoriginalEthernetstandard,includingCSMA/CDprotocol,Ethernetframe,fullduplex,flowcontrolandIEEE802.3Managementobjectsdefinedinthestandard.AsanintegralpartofEthernet,GigabitEthernetalsosupportstrafficmanagementtechnology,whichguaranteesthequalityofserviceonEthernet.ThesetechnologiesincludeIEEE802.1Player2priority,layer3priorityQoScodingbits,specialServiceandResourceReservationProtocol(RSVP).
GigabitEthernetalsoutilizesIEEE802.1QVLANsupport,fourth-levelfiltering,andGigabitthird-levelswitching.GigabitEthernetwasoriginallydesignedasaswitchingtechnology,usingopticalfiberastheuplinkforconnectionsbetweenbuildings.Later,intheconnectionofserversandbackbonenetworks,GigabitEthernethasbeenwidelyused.DuetotheintroductionoftheIEEE802.3abstandard(GigabitEthernetstandardusingcategory5andaboveunshieldedtwistedpair),GigabitEthernetcanbeused.Applicabletoanylarge,mediumandsmallenterprisesandinstitutions.
GigabitEthernethasdevelopedintoamainstreamnetworktechnology.Largeenterprisesaslargeastensofthousandsofpeople,smallandmedium-sizedenterprisesassmallasdozensofpeople,willuseGigabitEthernettechnologyasthepreferredhigh-speednetworktechnologywhenbuildingcorporateLANs.GigabitEthernettechnologyisevenreplacingATMtechnology,becomingthemainforceintheconstructionofmetropolitanareanetworks.
Features
1.GigabitEthernetprovidesaperfectmigrationpath,fullyprotectingtheinvestmentintheexistingnetworkinfrastructure.GigabitEthernetwillretainIEEE802.3andEthernetframeformatsand802.3managedobjectspecifications,sothatenterprisescanupgradetogigabitperformancewhileretainingexistingcables,operatingsystems,protocols,anddesktopapplicationsProgramandnetworkmanagementstrategiesandtools;
2.ComparedwiththeoriginalbackbonenetworksolutionssuchasFastEthernet,FDDI,andATM,GigabitEthernetprovidesanoptimalpath.Atleastfornow,itisareliableandeconomicalwaytoimprovethebackboneconnectionbetweentheswitchandtheswitchandtheconnectionbetweentheswitchandtheserver.Networkdesignerscanbuildahigh-speedinfrastructurethateffectivelyuseshigh-speed,mission-criticalapplicationsandfilebackups.NetworkmanagerswillprovideuserswithfasteraccesstotheInternet,Intranet,MetropolitanAreaNetworkandWideAreaNetwork.
3.TheIEEE802.3workinggroupestablishedthe802.3zand802.3abGigabitEthernetworkinggroups,whosetaskistodevelopGigabitEthernetstandardsthatmeetdifferentneeds.Thisstandardsupportsfull-duplexandhalf-duplex1000Mbps,andthecorrespondingoperationadoptsIEEE802.3EthernetframeformatandCSMA/CDmediaaccesscontrolmethod.GigabitEthernetisalsobackwardcompatiblewith10BaseTand100BaseT.Inaddition,theIEEEstandardwillsupportmultimodefiberswithamaximumdistanceof550meters,single-modefiberswithamaximumdistanceof70kilometers,andcoppercableswithamaximumdistanceof100meters.GigabitEthernetfillsinthedeficienciesofthe802.3Ethernet/FastEthernetstandard.
Construction
TheGigabitEthernetnetworkiscomposedofGigabitswitches,Gigabitnetworkcards,andintegratedwiringsystems.Thegigabitswitchformsthebackboneofthenetwork.Thegigabitnetworkcardisinsertedintotheserverandconnectedtotheswitchthroughawiringsystem.Therecanalsobemany100Mswitchesunderthegigabitswitch,andthe100Mswitchisconnectedtotheworkstation.Thisistheso-called"100MTothedesktop".Insomeprofessionalgraphicsproductionandvideo-on-demandapplications,"GigabittoDesktop"mayalsobeused,andaGigabitswitchisusedtoconnecttoaworkstationwithaGigabitnetworkcard,whichmeetsthedemandforhighbandwidthunderspecialapplications.
Beforebuildinganetwork,whethertouseGigabitor100M,wemuststartfromtheactualsituation,startfromtheapplication,andconsiderwhatfunctionsthenetworkshouldhave.Differentapplicationshavedifferentrequirements,andthereisalmostnonetworkwithasingleservice.However,amongthevariousbusinesses,theproductivebusinessisdefinitelythehighestpriority.Ifvoiceistransmittedoverthenetwork,thenvoiceservicesalsoneedtobeprioritized.Ifthedemandforbusinesspriorityishigh,thenetworkmusthaveQoSguarantees.Suchanetworkmustbeintelligent.Theswitchportcanidentifywhattypesofservicesarepassing,andthenqueueupdifferentservices,andallocatedifferentbandwidthsfordifferentservices,soastoensuretheoperationofkeyservices.Thedataserviceitselfisintelligent,anditcanbetransmittednomatterhowmuchbandwidthitis,justthelengthoftime,butthevoiceorvideoisnotthesame.Ifthebandwidthissmall,itwillbedifficulttohearimmediately,ortheimagewillbejittery.notallowed.SoQoSisveryimportant.Forapuredatanetwork,thedemandforQoSisverylow.Whenplanningthenetwork,youmustfirstunderstandwhichfunctionsarenecessaryandwhichcannotbeconsidered.Forexample,multicastingisoneofthemoreimportantfeatures.Ifimagesneedtobetransmittedonthenetwork,andthenetworkdoesnothavethecharacteristicsofmulticasting,thebandwidthwasteofthenetworkwillbeveryserious,orevenimpossibletoachieve.
InternationalStandard
InJanuary1997,thefirstdraftofIEEE802.3zwaspassed;
InJune1997,thedraftV3.1waspassed.Thefinaltechnicaldetailsareformulatedhere;
InJune1998,theIEEE802.3zstandardwasformallyapproved;
InJune1999,theIEEE802.3abstandard(ie1000Base-T)wasformallyapproved,YoucanusetwistedpaircablesforGigabitEthernet.
TheGigabitEthernetstandardmainlytargetsthreetypesoftransmissionmedia:single-modefiber;long-wavelaseronmulti-modefiber(called1000BaseLX),short-wavelaseronmulti-modefiber(called1000BaseSX));1000BaseCXmedium,whichcanbetransmittedonabalancedshielded150ohmcoppercable.The1000BaseTstandardsimulatedbytheIEEE802.3zcommitteeallowsthetransmissiondistanceofGigabitEthernetonCategory5,Super5,andCategory6UTPtwisted-pairlinestobeextendedto100meters,sothatmostofthewiringinthebuildingadoptsCategory5UTPtwistedpaircableguaranteestheuser'spreviousinvestmentinEthernetandFastEthernet.Fornetworkadministrators,thereisnoneedtoacceptnewtraining.WiththeknowledgeofEthernetnetworks,theycanmanageandmaintainGigabitEthernet.
ThestandardizationofGigabitEthernetincludesthreemainmodules:encoding/decoding,transceiver,andnetworkmedia.Differenttransceiverscorrespondtodifferentnetworkmediatypes.When1000BASE-LXisbasedonthe1300nmsingle-modeopticalcablestandard,ituses8B/10Bencodinganddecoding,andthemaximumtransmissiondistanceis5000meters.1000BASE-SXisbasedon780nmFibreChanneloptics,using8B/10Bencodinganddecodingmethods,using50micronor62.5micronmultimodeopticalcables,andthemaximumtransmissiondistanceis300metersto500meters.TheSCtypeopticalfiberconnectorusedtoconnecttheopticalfiberisofthesamemodelastheconnectorusedinFastEthernet100BASEFX.1000BASE-CXisastandardbasedoncoppercables,using8B/10Bencodinganddecodingmethods,withamaximumtransmissiondistanceof25meters.1000BASE-Tisbasedonunshieldedtwistedpairtransmissionmedium,using1000BASE-TcopperphysicallayerCopperPHYencodinganddecodingmethod,thetransmissiondistanceis100meters.1000BASE-Tusesall4twistedpairsintransmissionandworksinfullduplexmode.ThisdesignusesPAM-5(5-levelpulseamplificationmodulation)encodingtotransmit250Mbpsoneachpair.Two-waytransmissionrequiresthatallfourwire-pairtransceiverportsmustuseahybridmagneticfieldcircuit.Becauseaperfecthybridmagneticfieldcircuitcannotbeprovided,itisimpossibletocompletelyisolatethetransmittingandreceivingcircuits.Anysendingandreceivinglineswillechotheequipment.Therefore,toachievetherequirederrorrate(BER),theechomustbecanceled.1000BASE-Tcannotfilterthefrequencybandsabove125MHz,buttheuseofscramblingtechnologyandtrelliscodingcanfilterthefrequencybandsafter80MHz.InordertosolvethelimitationofCategory5linesduetonear-endcrosstalkinsuchahighfrequencyrange,appropriatesolutionsshouldbeadoptedtooffsetthecrosstalk.
TheoriginalGigabitEthernetusedhigh-speed780nmfiberchannelopticalcomponentstotransmitsignalsonopticalfibers,andused8B/10Bencodinganddecodingmethodstoachieveserializationandrestorationofopticalsignals.ThedataoperatingrateofFibreChanneltechnologyis1.063Gbps,whichwillbeincreasedto1.250Gbpsinthefuture,enablingthedataratetoreachacomplete1000Mbps.Forlongerconnectiondistances,1300nmopticalcomponentswillbeused.Inordertoadapttothedevelopmentofsilicontechnologyanddigitalsignalprocessingtechnology,amedium-independentlogicalinterfaceshouldbeestablishedbetweentheMAClayerandthePHYlayer,sothatGigabitEthernetcanworkinanunshieldedtwistedpaircablesystem.Thislogicalinterfacewillbeapplicabletotheencodingmethodofunshieldedtwistedpaircablesystemsandisindependentoftheencodingmethodoffiberchannel.ThefollowingfigureillustratesthecompositionofGigabitEthernet.
GigabitEthernet
Therearenotmanyconditionsforupgrading10Mand100MnetworkstoGigabit.Themostimportantthingistheintegratedwiringconditions.GigabitEthernetreferstothebandwidthofthenetworkbackbone,andthebackbonecablingsystemmustmeettherequirementsofGigabitEthernet.Iftheoriginalnetworkcoversmultiplebuildingsseparatedbyseveralhundredmeterstoseveralkilometers,theoriginalbackbonewiringgenerallyusesmulti-modeorsingle-modefiber,whichcanmeettherequirementsofagigabitbackbone,andthereisnoneedtore-laythefiber.Whenthedistancebetweenbuildingsislessthan550meters,generallylayingrelativelyinexpensivemulti-modeopticalfibercanmeettheneedsofGigabitEthernet.
Iftheoriginalnetworkonlycoversonebuilding,andthedistancebetweenthefurthestnetworknodeandthenetworkcenterisnomorethan100meters,theoriginalCategory5orCategory5cablingsystemcanbeused.IftheoriginalwiringsystemdoesnotmeettheCategory5standard,orifabus-typewiringsystemisusedinsteadofastar-typewiringsystem,thenCategory5linesmustbere-routed.
ToupgradetoGigabitEthernet,youmustfirstupgradethenetworkbackboneswitchtoGigabittoincreasethedatatrafficthatthenetworkbackbonecanwithstand,soastoachievethepurposeofacceleratingthenetworkspeed.Theprevious100Mswitcheswereusedasbranchswitches,andtheprevioushubscanbeusedwherethereareinsufficientwiringpoints.TherearemanyGigabitswitchproducts,whichcanbeselectedaccordingtoactualconditionssuchasnetworkrequirementsandbudgets.
Theserveronthenetworkneedstohandlealotofdata.Ifthenetworkbackboneisupgradedtogigabit,buttheservernetworkcardisstillatthelevelof100M,theservernetworkcardwillbecomethebottleneckofthenetwork,andgigabitmustbeusedThenetworkcardcaneliminatethisbottleneck.Thesolutionistoaddagigabitnetworkcardtotheoriginalserver.Notethat64-bitPCIGigabitnetworkcardsshouldbeselectedfirst,anditsperformanceishigherthanordinaryPCIGigabitnetworkcards.Gigabitnetworkcardcanbeselectedaccordingtoactualconditionssuchasnetworkrequirementsandbudget.
Thebackboneofthenetworkhasbeenupgraded,andthebranchesofthenetworkshouldbeupgradedaccordingly.Iftheoriginalusercomputerhasalreadyinstalleda10M/100Madaptivenetworkcard,youdon’tneedtoupgradethenetworkcard,justconnectthenetworkcardtoa100Mswitch;iftheoriginal10Mbpsnetworkcardisused,youneedtochangethenetworkcardto10M/100Madaptivenetworkcard,soastoincreasethespeedofworkstationsaccessingtheserver.
Prospectforecast
Itisestimatedthatbefore2005,thedatatransmissionvolumewillincreaseby3timeseachyear,andwillexceedthevoicetransmissionvolumethatyear,becomingthemaintransmissionmethodofglobalcommunicationnetwork.Inthefaceofever-increasingdatastreamsandmultimediaservices,themarketscaleofhigh-endnetworkproductswithlarge-capacity,high-speed,andmulti-functionmoduleswillcontinuetoexpand.ItisforeseeablethatthemarketshareofGigabitEthernetswitcheswillbecomelargerandlarger.WiththedevelopmentoftheInternetandtheemergenceofendlessapplicationsonthenetwork,10GigabitEthernetwillbethemainstreaminthefuture,andGigabitEthernetwillstillbethemainstreaminthemarket.
Technicaladvantages
Inordertomaintainthemaximumcollisionareawithadiameterof200metersandtheminimumCSMA/CDcarriertimeinthelocalareanetwork,theEthernettimeslicehasbeenextendedfrom512bitsto512bytes(4096bits),theminimumframelengthbecomes512bytes,andthemaximumframelengthisstill1518bytes.ThecarrierextensionfeaturesolvestheinherenttimingproblemofCSMA/CDwithoutmodifyingtheminimumpacketsize.Althoughthesechangesmayaffecttheperformanceofsmallinformationpackets,thiseffecthasbeenoffsetbyacharacteristiccalledpacketbursttransferintheCSM/CDalgorithm.ThebiggestadvantageofGigabitEthernetisitscompatibilitywithexistingEthernet.
Like100M-bitEthernet,GigabitEthernetusesthesameframeformatandframesizeas10M-bitEthernet,andthesameCSMA/CDprotocol.ThismeansthatthemajorityofEthernetuserscanupgradetheexistingEthernetsmoothlyandwithoutinterruptionwithoutaddingadditionalprotocolstacksormiddleware.Atthesametime,GigabitEthernetalsoinheritsotheradvantagesofEthernet,suchashighreliabilityandeasymanagement.
Comparedwithothertechnologies,GigabitEthernethastheadvantageoflargebandwidthandstillhasroomfordevelopment.Therelevantstandardsorganizationsareformulatingtechnicalspecificationsandstandardsfor10GEthernet.Atthesametime,prioritycontrolmechanismsandprotocolstandardsbasedontheEthernetframelayerandIPlayer,aswellasvariousQoSsupporttechnologieshavegraduallymatured,providingafoundationfortheimplementationofapplicationsrequiringbetterservicequality.Withtheadvancementofopticalfibermanufacturingandtransmissiontechnology,thetransmissiondistanceofGigabitEthernetcanreachupto100kilometers,whichmakesitgraduallybecomeatechnologychoiceforbuildingmetropolitanareanetworksandevenwideareanetworks.
TheadvantageofusingGigabitEthernetinthebackboneisthatGigabitEthernetwillprovide10timestheperformanceofFastEthernetandiscompatiblewiththeexisting10/100Ethernetstandard.Atthesametime,thevirtualnetworkstandard802.1Qandprioritystandard802.1pdevelopedfor10/100/1000Mbpshavebeenpromoted,andthegigabitnetworkhasbecomethemainstreamtechnologythatformsthebackboneofthenetwork.
ThefirstGigabitEthernetstandard802.3,whichwasformulatedinJune1998,targetsfull-duplexlinksusingopticalfibercablesandshort-distancecoppercables.Thestandard802.3abforhalf-duplexandremotecopperwirecableswasintroducedin1999.
Thehigh-speedmulti-layerdatapacketforwardingcapabilityofGigabitEthernetisapowerfulexamplethatGigabitEthernettechnologycanprovidethebestperformance-to-priceratio.Notonlythat,GigabitEthernettechnologyisalsoverybeneficialforreducingthelong-termcostofownershipofthenetwork.
Switchingtechnology
Sincetheendof1996,somecompanieshavesuccessivelyintroducedswitchproductsthatintegratelayer2switchingandlayer3routing.Thistechnologyiscalled"multi-layerswitching(multilayerswitching)".Itaddsroutinglayerservicestolayer2switchingtechnology,supportsselectivebroadcastandmulticastsuppression,supportspacketforwardingandfirewallfunctionsbetweenVLANsandVLANs,andfullysupportsTCP/IPandIPXrouting.
Afternearly4yearsofdevelopment,thesefunctionshavebeencontinuouslyimprovedandstrengthened,makingtheperformance-priceratioofmulti-layerswitches8to16timeshigherthantraditionalrouters.Thenewgenerationofmulti-layerswitcheswithGigabitEthernetswitchingtechnologyasthecore,canprovidemoreattractiveperformance-priceratio,andisthemostidealswitchthatcanprovidemulti-layerswitchingindepartmentalnetworksanddatacenternetworkstoreplacetraditionalrouters.Atthesametime,itsdirecttransmissiondistancehasnowreached130kilometers,whichcanfullyrealizealargeenterpriseLANwithGigabitEthernetasthebackbone,andthebackbonetransmissionrateis2Gbps(fullduplexmode).
ThemainfactorthatpromotesthedevelopmentoftechnologyThebiggestfactorthatpromotesthedevelopmentofhigh-speedmulti-layerswitchingtechnologyisthemassdeploymentoftheInternetandIntranetusingcheap10/100Madaptivenetworkcards.Thenetworkhasbecomefartherandfartherawayfromthetraditionalc/scomputingmodel'shierarchicalstructure,andthetraditional80/20trafficruleofthec/smodelhasbecomeathingofthepast.Intermsofnetworkdesign,thetraditionalrouterplusHuborLayer2switchnetworkdeploymentmodelwillalsobecomehistory.
Inaddition,Intranetsupportsavarietyofmorecomplexandbandwidth-sensitivemultimediadatastreams,suchasdata,files,pictures,animation,sound,andvideo.Anintranetenduserrequiresatleast50%to100%morebandwidththananon-Intranetuser.Atthesametime,broadbandaccesshasbecomeadevelopmenttrend.
AnotherissueworthnotingisthatprovidinguserswithafastEthernetconnectioncanprovidemorebandwidthmargintohandlesuddentraffic,whichisunmatchedby10BASE-Ttechnology.BursttrafficisoneofthecharacteristicsofIPnetworkapplications.LowcostandhighbandwidthmakeFastEthernetwidelyusedonboththeusersideandtheserverside.
Inordertostrikeabalancebetweennon-blockingandtheabilitytohandlesuddentrafficflows,thenewgenerationofswitchplatformsmustprovidebackboneconnectionsthatare8-16timesfasterthantheuser’srequestconnection.ThenetworkbackbonejustsatisfiestheservicerequestofthefastEthernetconnectionontheuserside.Thisisveryimportanttoadequatelyhandlebursttraffic.
Atthesametime,incampusnetworksormetropolitanareanetworks,nomatterhowmanynetworklayersarespanned,randomintranettrafficisrequiredtoprovideend-to-endconsistenthighperformance.Inordertoachievethis,itistheonlysolutiontohavebothhigh-performancelayer2andlayer3forwardingcapabilitiesinaswitch.
Thenon-blockingcapabilityandselectiveforwardingfunctionarethemainrequirementsofusers.Variousveryeffectivenetworkmanagementtoolsenablenetworkadministratorstoeffectivelyandefficientlyinjectbusinessstrategiesintotheforwardingengine,anditsperformancecanbemonitoredinrealtimethroughnetworkmanagementsoftware.Thiswillfundamentallyhelpusersdetermineanddelivertherequirednetworkservicesaccordingtothecompany'sshort-termandlong-termbusinessdevelopmentneeds.ThenewgenerationofGigabitEthernetswitchessupportthesefeaturesandservices,aswellascommonroutingprotocolssuchasIP/RIPorIP/OSPF.Thisalsogreatlyreducesthecomplexityofnetworkequipment.
Objectiveprinciples
Thehighperformanceofthenetworksystemrequiresthecoreswitchtomeettherequirementsofthemassivedataexchangeofthenetworkcenter,andthecommunicationlinkbandwidthoftheuplinkcentercanmeettheperformancerequirementsoftheapplicationonthenetwork.Regardlessofwhetheritisanenterprisenetwork,ametropolitanareanetwork,orawideareanetwork,theinformationapplicationsonitaredevelopingatanunprecedentedspeed,andnewmultimediaapplicationsandnewdataapplicationsplacehigherrequirementsonbandwidth.Inthecaseofenterprisesgenerallyadoptingtheintranetnetworkmodel,itsWWWserver,FTPserver,LotusNotesgroupwareapplicationserver,NovellServerandotherserverclusterssupporttheentireenterprise'sinformationserviceenvironment.Theclientapplicationsoftwareofusersinvariousdepartmentsoftheenterpriseaccessesthecentralserverthroughthenetwork,requestsapplications,andqueriesthedatabase.Theloadflowofthenetworkismainlythedataexchangefromtheedgedevicetothecore.Withthedevelopmentofenterprisebusiness,theexpansionofthenetworkscale,andtheincreaseintheamountofinformationexchangeoftheapplication,theenterprisenetworkusuallyfirstoccursinthecoreofthecommunicationbottleneckphenomenon.ToimprovethenetworkdataexchangeperformanceoftheenterprisecampusLAN,thefirststepistoexpandtheexchangeperformanceofthecoreswitchandincreasethedatacommunicationbandwidthfromtheedgedevicetothecoretoreducethebottleneckoftheentirenetworkandimprovetheperformanceandefficiencyofapplicationsoftware.Therefore,intheprincipleofdesigninganenterprisecampusLAN,weshouldfirstconsiderthedataexchangeprocessingcapabilitiesofthecoreequipmentrequiredbythenetworkscale,andthelinkbandwidthfromtheedgeequipmenttothecore.
Reliabilityandavailability
Thehighreliabilityofequipmentandhighavailabilityofthesysteminthenetworksystemdesign;allkeycomponentsofthecoreswitcharerequiredtoachieveredundancyandcanbereplacedonline(plug),therecoverytimeofthefaultiscompletedwithinasecondinterval.Themulti-levelfault-tolerantdesignfurtherimprovestheavailabilityofthesystembasedonthehighreliabilityofasingledevice.
Asfarasenterpriseapplicationsareconcerned,itusesadvancedcomputer,networkandotherinformationtechnologiestorealizeautomaticcontroloftheproductionprocessandpaperlessofficeautomation,whichimprovestheefficiencyandlevelofproductionandmanagementoftheenterprise.Theinfrastructuresupportingenterpriseapplicationsistheenterprise'scampusnetwork.Itsworkingconditionswilldirectlyaffecttheenterprise'sofficeapplicationenvironment,businessenvironmentsuchastransaction,production,development,design,financialmanagement,partsmanagementandotherenvironments,informationretrieval,databasequery,Internetbrowsingandothernecessaryservicefacilitiestosupportthenormaloperationoftheenterprise.Thereliabilityrequirementofthenetworkistheprimaryconditiontoensurethenormaloperationoftheenterpriseapplicationenvironment.Whilethenetworkrequiresreliability,italsorequiresthenetworktohavehighavailability.Thechoiceofnetworkequipment,especiallythecorechassis-typeequipment,shouldbeabletoconfigureredundantcomponents.Thereisnosinglepointoffailureforkeycomponents.Thatistosay,componentssuchasswitchpowersupplies,fans,switchingengines,andmanagementmodulescanberedundantlybackedup.Thedamageofanypartofoneofthemwillnotaffectthenormaloperationoftheequipmentandwillnotaffectthenetworkconnection.Anotherrequirementforthereliabilityandfaulttoleranceofthenetworkequipmentisthatwhenthedamagedpartsoftheequipmentarereplaced,thereisnoneedtoshutdown,andthereisnoneedtorestartafterreplacingtheparts.Thatistosay,thereplacementofthepartscanbeoperatedonline,whichcanreducethedowntime.Tothesmallest.Ontheprincipleofdesigningenterprisecampusnetworks,itisveryimportanttoimprovetheprinciplesofhighreliabilityandhighavailabilityofthenetwork.Notonlytheequipmentcomponentsarerequiredtoberedundant,butalsothenetworklinkredundancyisrequired,whichcancombinethephysicallayer,linklayerandThethirdlayeroftechnologyisimplementedtoensurethatthenetworkcanprovideinformationaccessservicesatanytimeandanyplace.
Scalability
Thescalabilityrequirementsofnetworkdesignincludethescalabilityofswitchhardwareandtheabilityofthenetworktoimplementnewapplications.Flexiblescalabilityrequirementsforcoreswitches:Thecoreswitchesshouldhaveflexibleportexpansioncapabilitiesandmoduleexpansioncapabilitiestomeettheexpansionofnetworkscale;atthesametime,improveperformancetomeethigherperformancerequirements.Abilitytosupportnewapplications:Theproducthasthetechnicalpreparationtosupportnewapplications,andcanimplementnewapplicationsquicklyandeasily.

Scaleandusers
Whendesigninganetworkplan,thefirstthingtodoistomeettheneedsofnetworkusersoftheexistingscale.Atthesametime,consideringfuturebusinessdevelopmentandscaleexpansion,thenetworkshouldbedesignedIthasflexibleexpansioncapabilitiesforuserports.Thecoreequipmentisthehuboftheentirenetwork.Theexpansionofthenumberofuserportsrequirestheadditionofequipmentintheedgeworkinggroupofthewiringcloset.Whentheedgeequipmentisadded,thenumberofportsconnectedtothecorebackboneequipmentisrequiredtoincreaseaccordingly.Therefore,thecoreequipmentshouldbeabletoincreasethenumberofmodules.Toflexiblyincreasethenumberofports.Thechassisdesignofthecoreequipmentshouldhaveastrongbackplanebandwidthandenoughloadslotcapacity.Fortheswitch,thecoreswitchingengineshouldbeabletoperformportdatapacketswitchingwithoutblockingunderthemaximumconfiguration,andtheexpansionofthemoduledoesnotaffecttheswitchingperformance.Theuseofadistributedswitchingstructureisthebestsolutiontorealizethisprinciple.Thedistributedswitchstructurerealizestheparalleldataexchangeprocessingoftheswitchesandoptimizestheperformanceofthenetwork.Thedistributedstructurecombininglocalandglobalswitchingreducesthecoreswitchingengine.pressure.Therefore,intheprincipleofdesigninglarge-scalecampusnetworks,distributedswitchesaregenerallyusedtoachieveflexiblemoduleandportexpansioncapabilities.
Security
Networksecurityisveryimportanttonetworkdesign.Reasonablenetworksecuritycontrolcaneffectivelyprotectandcontroltheinformationresourcesintheapplicationenvironment.Networkaccess,flexibleimplementationofnetworksecuritycontrolstrategies.Intheenterprisecampusnetwork,onlysystemadministratorshavethepowertooperateandcontrolkeyapplicationserversandcorenetworkequipment.Theapplicationclientonlyhastherighttoaccesssharedresources,andthenetworkshouldbeabletopreventanyillegaloperations.Itshouldbepossibletoperformpacketfilteringcontrolfunctionsbasedonprotocol,Macaddress,andIPaddressonthecampusnetworkequipment.Inthedesignoflarge-scalecampusnetworks,dividingvirtualsubnetscaneffectivelyisolatealargenumberofbroadcastsinthesubnetsontheonehand,andontheotherhandisolatethecommunicationbetweennetworksubnets,controlresourceaccessrightsandimprovenetworksecuritysex.Inthedesignofthecampusnetwork,thesecuritycontrolcapabilityofthenetworkmustbeemphasized,sothatthenetworkcanbeconnectedarbitrarily,andtheaccesstothenetworkcanbecontrolledfromthesecondandthirdlayers.
Manageability
Networkmanageabilityrequirements:anydeviceinthenetworkcanbecontrolledthroughthenetworkmanagementplatform,andnetworkequipmentstatus,faultalarms,etc.canallbemanagedthroughthenetworkmanagementTheplatformperformsmonitoring,simplifiesmanagementthroughthenetworkmanagementplatform,andimprovestheefficiencyofnetworkmanagement.
Innetworkdesign,itisessentialtochooseadvancednetworkmanagementsoftware.Networkmanagementsoftwareisusedinnetworkequipmentconfiguration,networktopologydisplay,networkequipmentstatusdisplay,networkequipmentfailureeventalarm,networktrafficstatisticsanalysisandbilling,etc.Theapplicationofnetworkmanagementsoftwarecanimprovetheefficiencyofnetworkmanagementandreducetheburdenonnetworkmanagementpersonnel.Thegoalofnetworkmanagementistoachievezeromanagement,astrategy-basedmanagementmethod,andnetworkmanagementisgloballycontrolledbythemanagementstrategyserverbyformulatingaunifiedstrategy.Theweb-basednetworkmanagementinterfaceisthedevelopmenttrendofnetworkmanagementsoftware,andtheflexibleoperationmodesimplifiestheworkofmanagementpersonnel.Inthedesignofthecampusnetworkequipmentselection,thenetworkequipmentisrequiredtosupportthestandardnetworkmanagementprotocolSNMP,whilesupportingtheRMON/RMONIIprotocol,andthecoreequipmentisrequiredtosupporttheRAP(remoteanalysisport)protocoltoimplementsufficientnetworkmanagementfunctions.Inprinciple,thedesignofthecampusnetworkshouldrequirethemanageabilityofequipment,whileadvancednetworkmanagementsoftwarecansupportnetworkmaintenance,monitoring,configurationandotherfunctions.
Standardizationoftheprotocol
Networkequipmentadoptsopentechnologyandsupportsstandardprotocols:standardprotocolsareusedtoprotectusers’investmentandimproveequipmentinteroperability.Theequipmentusedinnetworkdesignrequiresmainstreamtechnologyanddevelopedstandardprotocols,hasgoodinteroperability,andcansupportdifferentseriesofproductsofthesamemanufacturer,andseamlessinterconnectionandcommunicationbetweenproductsofdifferentmanufacturers.Ontheprincipleofdesigningthecampusnetwork,thespecialadvancedtechnologyofdifferentmanufacturers'productsmustbeused,andthestandardizationofequipmenttechnologyandprotocolmustbeemphasizedtoreduceequipmentinterconnectionproblemsandnetworkmaintenancecosts,sothatuserinvestmentcanbeeffectivelyprotected.
Itshouldbeconsideredwhethertheselectedequipmentisupgradeable.Afterthenewstandardappears,thesystemshouldbeabletoupgradetothenewstandard.Therefore,focusonthestatusofproductmanufacturersinthecorrespondingproductandtechnicalfieldsandtheirabilitytoparticipateinstandardization.
Intoday'sworld,thedevelopmentofcommunicationtechnologyandcomputertechnologyischangingwitheachpassingday.Networkdesignmustnotonlyadapttothetrendofnewtechnologydevelopment,ensuretheadvancednatureofthesystem,butalsotakeintoaccountthetechnicalmaturity,andreducetheriskscausedbyimmaturefactorsinnewtechnologiesandnewproducts.
Solution
ThebiggestadvantageofGigabitEthernetisitscompatibilitywithexistingEthernet.Like100M-bitEthernet,GigabitEthernetusesthesameframeformatandframesizeas10M-bitEthernet,andthesameCSMA/CDprotocol.Inthecampusnetworkbackbonenetwork,graduallyoccupyamajorposition.
Asafeatureofcampusnetworkapplications,mostapplicationsarenotsensitivetodelayandbandwidth,andcanautomaticallyidentifydelaychangesthroughtheTCP/IP"slowstart"mechanism,anddynamicallyadapttothebandwidthprovidedbyTCP,Someapplicationsrequirereal-timeservicetransmissionsupportandQoSserviceguarantee.Thispartoftheapplicationaccountsforasmallproportion.Withtheaccelerationofthemodernizationofteachingmethods,thegradualpopularizationofmultimediacoursewareproductiontools,andthegradualenrichmentofmultimediacourseware,theproportionisexpectedtograduallyincrease.Themainbottleneckofreal-timeservicetransmissionoverIPnetworkisthatroutersusesoftwaretorealizerouteidentification,calculationandpacketforwarding.Duetotheslowspeedofrouteidentificationanddataforwarding,thedelayanddelayjitterarelarge,thequalityofservice(QoS)cannotbeguaranteed.Sincethesecondhalfof1997,somecompanieshavesuccessivelyintroducednewwire-speedroutingswitchesthatusehardwarededicatedcircuits(ASIC)forroutingidentification,calculation,andforwarding.Thestructureofthiswire-speedroutingswitchissimilartothatoftheL2switch.IthasboththeL3routerpacketforwardingfunctionandtheL2switchingfunction.SomemanufacturersalsoaddsomeL4applicationlayerfunctions.
ToprovideQoSonthepacket-switchedIPnetwork,theservicemustbeclassified,andtheclassificationservice(CoS)mustbeimplemented.Equipmentmanufacturersgenerallyusecongestionmanagementtoensurenetworkperformanceandprovidetherequiredbandwidthforsomespecializedservices.OneapproachistouseRED(RandomEarlyLoss)todetectandintelligentlyidentifytheinstantaneoussurgeintraffictodistinguishitfromrealnetworkcongestiontoavoidnetworkcongestion.Byidentifyingtheservicecategory(802.1P)fromtheIPv4serviceclassificationidentifier(TOS)intheIPpacketheader,thepriorityofthedataflowisdetermined,andacertainqueuepriorityalgorithmisusedtoensuretheQoScapability.Youcanalsouseanaccesscontrollist(ACL)todefinepoliciesanddeterminethepriorityofdatastreams.Withtheadvancementoftechnology,itisforeseeablethatQoScapabilitiesonhigh-speedIPnetworkswillreachasimilarlevelofFR/ATMnetworks.
Onthebasisofanalyzingandcomparingtheperformance,price,andserviceofavarietyofL2/L3/L4wire-speedroutingswitchesinthemarket,atotalof11CajunP550RroutingswitchesfromLucent(Lucent)wereselectedasthecampusNetworkbackboneswitch.Itsmaintechnologyandperformanceindicatorsare:
Backplanecapacity45.76Gbps
Switchingthroughputcapacity22.88Gbps
Layer2switchingcapacity33,000,000pps
Layer3switchingcapacity18,000,000pps
MultipleL2/L3interfacemodules
Redundantfans,powersupplies
OpenTrunk/VLANinteroperability
CoS/QoS/RSVPsupport
Innetworkdesign,backboneswitchesareinterconnectedwitheachotherthroughGigabitEthernet.AllswitchesareequippedwithL3switchingenginetoimplementdistributedroutingstrategies,therebyreducingthepressureonL3routinganalysisandpacketforwardingofthecentralswitchandcontrollingthescopeofthebroadcastdomain.Thenetworkdesignandequipmentconfigurationcarefullyconsiderthephysicalandlogicalredundancyofequipment,linesandrouting,thefirewallsettingsandsecuritypoliciesofthenetworkcenterservergroup.
Technology
1000Base-TTechnology
WiththereleaseoftheNationalTechnicalSpecificationforGigabitEthernetSwitchEquipment,GigabitEthernetTheapplicationoftechnologyhasbeendevelopedbyleapsandbounds.
1000Base-T(GigabitEthernetimplementedonCategory5twistedpair)hasbecomeoneofthebestchoicesfornetworkmanagersduetothefollowingreasons.First,itmainlymeetstherapidlyincreasingdemandforbandwidthinexistingnetworks;secondly,inthesenetworks,emergingapplicationscontinuetoappear,andswitchesattheedgeofthenetworkarealsoincreasing.GigabitEthernetcanprotectthecompany'sexistinginvestmentsinEthernetandFastEthernetfacilities;third,itcanprovideasimple,effectiveandinexpensiveperformanceimprovementmethod,whilecontinuingtousealargenumberofexistingHorizontalcabletransmissionmedium.
1000Base-Ttechnologyprinciple
Transmissionmediaspecification
GigabitEthernetcanusetheexistingcablefacilities,sothatithasagoodperformancepriceCompare.Itcanbeusedonthenetworkinfloors,buildingsandcampusesbecauseitcansupportmultipleconnectionmediaandawiderangeofconnectiondistances.Inparticular,GigabitEthernetcanrunonthefollowingfourmedia:opticalfiber,withamaximumconnectiondistanceofatleast5kilometers;Modularfiber,withamaximumconnectiondistanceofatleast550meters;balanced,shieldedcoppercable,withamaximumconnectiondistanceofatleast25meters;Category5lines,withamaximumconnectiondistanceofatleast100meters.
TheIEEE802.3zGigabitEthernetstandardwasapprovedinJune1998.Itdefinesthreetransceiversforthreetransmissionmedia:1000Base-LX,1000Base-SXand1000Base-CX.Amongthem,1000Base-LXisusedtoinstallsingle-modeopticalfiber,1000Base-SXisusedtoinstallmulti-modeopticalfiber,and1000Base-CXisusedtobalanceandshieldcoppercables.Itcanbeusedforinterconnectionincomputerrooms.1000Base-LXtransceiverscanalsobeusedformultimodeopticalfibers,withatransmissiondistanceofatleast550meters.
GigabitEthernetLayering
Anotherspecialworkinggroup,IEEE802.3abhasdefinedthephysicallayerforrunningGigabitEthernetonthebasisofCategory5lines.TheIEEEStandardizationCommitteeapprovedthe1000Base-TstandardinJune1999.1000Base-Tcancontinuetousetheexistingcablefacilities,anditstipulatesthatthetransmissiondistanceontheCategory5linecanbeupto100meters.
Someotherimportantspecificationsof1000Base-Tmakeitalow-cost,hard-to-break,andgood-performancetechnology.Firstofall,itsupportsEthernetMACandisbackwardcompatiblewith10/100MbpsEthernettechnology;secondly,many1000Base-Tproductswillsupport100/1000auto-negotiationfunction,so1000Base-TcanbedirectlypassedthroughthefastEthernetnetworkUpgraderealization;third,1000Base-Tisahigh-performancetechnology,ittransmits10billionbits,ofwhichtherewillbenomorethanonewrongdatabit(biterrorrateislessthan10-10,whichisthesameas100Base-T'sbiterrorTherateiscomparable).
Cablespecification
1000Base-TstipulatesthatdatacanbetransmittedonCategory5balancedtwistedpaircables.TheANSI/EIA/TIA-568-A(1995)specifiestheperformanceofthefour-pairfive-categorytwistedpairused.Otherlinkperformanceparameters(returnlossandELFEXT)arespecifiedinTIA/EIA-TSB-95.ThestandardforCategory5cablesisstipulatedinISO/IEC11801:1995("InformationTechnology:GeneralCablesforUserFront-endEquipment").ThesecondeditionofISO/IEC11801:1995specifiessomeothercableperformanceparameterstosupportGigabitEthernet.
Physicalstructure
1000Base-TisspeciallydesignedtotransmitdataonCategory5twistedpaircables.Thetransmissionrateof1Gbpscanbeequivalentlyregardedasfourpairsoftwistedpairs,andthetransmissionrateofeachpairis250Mbps(250Mbps×4=1Gbps).
1000Base-Tand100Base-Tusethesametransmissionclockfrequency(125MHz),butuseamorepowerfulsignaltransmissionandencoding/decodingscheme,whichcanbecomparedto100Base-TonthelinkTtransmitstwiceasmuchdata.Thefollowingisacomparisonofthesetwotechnicalspecifications:
1000Base-T:125MHz×2bit=250Mbps
1000Base-TX:125MHz×2bit-symbol=125Mbit-symbol/s
Pleasenote:125Mbits-symbol/sisequivalentto100Mbps,because1000Base-Tusesa4B/5Bencoding-beforeputtingthesignalonthecablefortransmission,every4bitsThedataisconvertedinto5-bit-symbols;theeffectivebittransferrateis:125×4/5=100Mbps.
1000Base-Tencoding
Inordertocost-effectivelyuse4to5typesofUTP,IEEE802.3abdoesnotuse8B/10Bencoding,butdefinesalogicintheMACsublayerandPHYlayerTheinterfaceallowstheintroductionofmorecost-effectivecodingschemes.Duetothelimitationofavailablebandwidth,itisobviousthateachpairofCategory5UTPshouldnotexceed125Mbaud(whenCategory5UTPisat62.5MHz,itsACRis30.6dB).Takingintoaccountthatitcancover28=256andminimizethenumberofsymbolsinthemultiplexsystem,afive-level(quinary)codeisadopted,thatis,8B/4Quinary.Inthisway,(1000/4)×(4/8)=125Mbaudcanmeetthelimitationofavailablebandwidth.
Iffour-level(quartemary)codingisused,theaboverequirementscanalsobemet,anditcanalsocover28=256,buttheredundantoneinthefive-level(quinary)codingcanbeusedfortheotherfourlevelsErrorcorrectioncode.
Therecent1000Base-TwhitepaperoftheGigabitEthernetAlliancerecommendstheuseofPAM-5code,eachsymbol(takeoneof+2,+1,0,-1,-2)correspondstotwodigitsBinaryinformation(fourlevelsrepresenttwobits,onelevelisusedforforwarderrorcorrectioncode).Theforwarderrorcorrectioncodeadoptsthe4-dimensional8-stateTrellisforwarderrorcorrectioncode.Therealizationofthesemainlydependsonintegratedcircuittechnologyanddigitalsignalprocessing(DSP)technology.
1000Base-TcansupporttheexistingFastEthernetandV.90/56Kmodemtechnologiesthathavebeentestedinpractice,therebyachievingagoodperformance-priceratio.AdvancedDSPsthatimplementsignaltransmissionandencoding/decodingtechniquesin802.3FastEthernetandV.90or56Kmodemscanalsobeusedtoimplement1000Base-T.
Developmentadvantages
GigabitEthernetisanewtypeofhigh-speedlocalareanetwork,whichcanprovide1Gb/scommunicationbandwidth,andadopts10/100MEthernethasthesameCSMA/CDprotocol,frameformatandframelength,soitcanachieveasmoothandcontinuousnetworkupgradeonthebasisoftheoriginallow-speedEthernet,whichcanmaximizetheprotectionoftheuser'spreviousinvestment.
Conclusion
AsmoreandmoredesktopcomputersandworkgroupsupgradetoFastEthernet,thecentralizedbusinessofthebackboneofthenetworkwillincreasesubstantially.Inordertohandlethiskindofbusiness,allnewbackboneswitchesshouldsupportGigabitEthernetuplinks.GigabitEthernetswitchesinthebackbonenetworkcanbeusedtoconnecthightransactionrateserversandnetworksegmentswitchesforcentralizedFastEthernetworkinggroups.IftheopticalfibernetworkconnectionmodeofGigabitEthernetsolvesthehigh-speedconnectionbetweenbuildings,then1000Base-TGigabitEthernettechnologyisusedtosolvethehigh-speedconnectionbetweenfloorsandevenbetweenoffices.
Othertypes
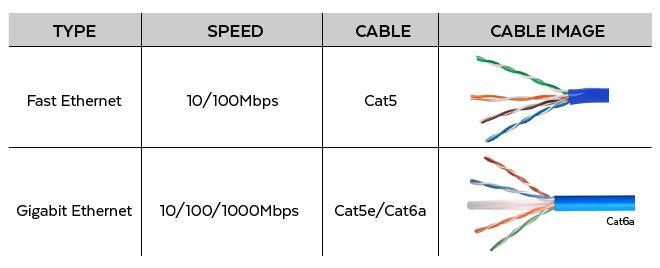
StandardEthernet
Atthebeginning,theEthernetonlyhasathroughputof10Mbps,anditusescarriersensemultipleaccesswithcollisiondetection(CSMA/CD,CarrierSenseMultipleAccess/CollisionDetection)accesscontrolmethod,thisearly10MbpsEthernetiscalledstandardEthernet.Ethernetcanusethickcoaxialcable,thincoaxialcable,unshieldedtwistedpair,shieldedtwistedpairandopticalfiberandothertransmissionmediaforconnection,andintheIEEE802.3standard,differenttransmissionmediahavebeenformulated.Physicallayerstandards.Inthesestandards,thefrontnumberindicatesthetransmissionspeed,theunitis"Mbps",thelastnumberindicatesthelengthofasinglesegmentofthenetworkcable(thebaseunitis100m),Basemeans"baseband",andBroadmeans"broadband".
·10Base-5usesathickcoaxialcablewithadiameterof0.4inchesandanimpedanceof50Ω,alsoknownasthickcableEthernet,themaximumnetworksegmentlengthis500m,thebasebandtransmissionmethod,thetopologyisabustype;10Base-Themainhardwareequipmentofthe5-groupnetworkincludes:thickcoaxialcable,EthernetcardwithAUIsocket,repeater,transceiver,transceivercable,terminator,etc.
·10Base-2usesathincoaxialcablewithadiameterof0.2inchesandanimpedanceof50Ω,alsoknownasthincableEthernet.Themaximumnetworksegmentlengthis185m,thebasebandtransmissionmethod,andthetopologyisbustype;10Base-2Themainhardwareequipmentofthenetworkincludes:thincoaxialcable,EthernetcardwithBNCsocket,repeater,T-connector,terminator,etc.
·10Base-Tusestwisted-paircable,themaximumlengthofthenetworksegmentis100m,andthetopologyisstar-shaped;themainhardwareequipmentofthe10Base-Tnetworkincludes:Category3orCategory5unshieldedtwistedpaircable,EthernetcardswithRJ-45sockets,hubs,switches,RJ-45plugs,etc.
·1Base-5usestwisted-paircable,themaximumnetworksegmentlengthis500m,andthetransmissionspeedis1Mbps;
·10Broad-36usescoaxialcable(RG-59/UCATV),themaximumspanofthenetworkis3600m,andthemaximumlengthofthenetworksegmentis1800m,whichisabroadbandtransmissionmethod;
·10Base-Fusesopticalfibertransmissionmedium,andthetransmissionrateis10Mbps.
FastEthernet
Withthedevelopmentofthenetwork,thetraditionalstandardEthernettechnologyhasbeenunabletomeettheincreasingdemandfornetworkdatatrafficspeed.BeforeOctober1993,forLANapplicationsrequiringdatatrafficabove10Mbps,onlytheopticalfiberdistributeddatainterface(FDDI)wasavailable,butitwasaveryexpensiveLANbasedon100Mpbsopticalcable.InOctober1993,GrandJunctionlaunchedtheworld'sfirstfastEthernethubFastch10/100andnetworkinterfacecardFastNIC100,andthefastEthernettechnologywasofficiallyapplied.Subsequently,Intel,SynOptics,3COM,BayNetworksandothercompanieshavealsolaunchedtheirownfastEthernetdevices.Atthesametime,theIEEE802engineeringgroupalsoconductedresearchonvariousstandardsof100MbpsEthernet,suchas100BASE-TX,100BASE-T4,MII,repeater,fullduplexandotherstandards.InMarch1995,IEEEannouncedtheIEEE802.3u100BASE-TFastEthernetstandard(FastEthernet),andthusbegantheeraofFastEthernet.
ComparedwiththeoriginalFDDIworkingat100Mbpsbandwidth,FastEthernethasmanyadvantages.ThemostimportantthingisthatFastEthernettechnologycaneffectivelyprotecttheuser’sinvestmentintheimplementationofwiringinfrastructure.ItsupportsTheconnectionofcategory3,4,5twistedpairandopticalfibercaneffectivelyutilizetheexistingfacilities.TheshortcomingsofFastEthernetareactuallytheshortcomingsofEthernettechnology,thatis,FastEthernetisstillbasedonCSMA/CDtechnology.Whenthenetworkloadisheavy,itwillcauseadecreaseinefficiency.Ofcourse,thiscanbecompensatedbyswitchingtechnology.The100MbpsfastEthernetstandardisdividedintothreesub-categories:100BASE-TX,100BASE-FX,and100BASE-T4.
·100BASE-TX:isafastEthernettechnologythatusesCategory5data-levelunshieldedtwistedpairorshieldedtwistedpair.Itusestwopairsoftwistedpairs,onepairforsendingandonepairforreceivingdata.The4B/5Bencodingmethodisusedinthetransmission,andthesignalfrequencyis125MHz.ComplywithEIA586'sCategory5wiringstandardandIBM'sSPTCategory1wiringstandard.UsethesameRJ-45connectoras10BASE-T.Itsmaximumnetworksegmentlengthis100meters.Itsupportsfull-duplexdatatransmission.
·100BASE-FX:ItisakindoffastEthernettechnologythatusesfiberopticcable,whichcanusesingle-modeandmulti-modefiber(62.5and125um).Themaximumdistanceofmultimodefiberconnectionis550meters.Themaximumdistanceofsingle-modefiberconnectionis3000meters.The4B/5Bencodingmethodisusedinthetransmission,andthesignalfrequencyis125MHz.ItusesMIC/FDDIconnector,STconnectororSCconnector.Itsmaximumnetworksegmentlengthis150m,412m,2000morlongerto10kilometers,whichisrelatedtothetypeoffiberusedandworkingmode,anditsupportsfull-duplexdatatransmission.100BASE-FXisparticularlysuitableforapplicationsinenvironmentswithelectricalinterference,large-distanceconnections,orhigh-securityenvironments.
·100BASE-T4:ItisakindoffastEthernettechnologythatcanuse3,4,5typesofunshieldedtwistedpairorshieldedtwistedpair.100Base-T4uses4pairsoftwistedpairs,ofwhichthreepairsareusedtotransmitdataatafrequencyof33MHz,andeachpairworksinhalf-duplexmode.ThefourthpairisusedforCSMA/CDconflictdetection.The8B/6Tencodingmethodisusedinthetransmission,andthesignalfrequencyis25MHz,whichconformstotheEIA586structuredwiringstandard.ItusesthesameRJ-45connectoras10BASE-T,andthemaximumnetworksegmentlengthis100meters.
10GigabitEthernet
The10GigabitEthernetspecificationisincludedinthesupplementarystandardIEEE802.3aeoftheIEEE802.3standard.ItextendstheIEEE802.3protocolandMACspecificationtosupport10Gb/sThetransferrate.Inaddition,throughtheWANinterfacesublayer(WIS:WANinterfacesublayer),10GigabitEthernetcanalsobeadjustedtoalowertransmissionrate,suchas9.584640Gb/s(OC-192),whichallows10GigabitEthernetequipmentiscompatiblewiththeSynchronousOpticalNetwork(SONET)STS-192ctransmissionformat.
·10GBASE-SRand10GBASE-SWmainlysupportshortwave(850nm)multimodefiber(MMF),andthefiberdistanceis2mto300m.
10GBASE-SRmainlysupports"darkfiber".Darkfiberreferstoanopticalfiberthathasnolightpropagationandisnotconnectedtoanyequipment.
10GBASE-SWismainlyusedtoconnectSONETequipment,anditisusedforremotedatacommunication.
·10GBASE-LRand10GBASE-LWmainlysupportlong-wave(1310nm)single-modefiber(SMF)withafiberdistanceof2mto10km(about32,808feet).
When10GBASE-LWismainlyusedtoconnectSONETequipment,
10GBASE-LRisusedtosupport"darkfiber".
·10GBASE-ERand10GBASE-EWmainlysupportultra-longwave(1550nm)single-modefiber(SMF)withafiberdistanceof2mto40km(approximately131,233feet).
10GBASE-EWismainlyusedtoconnectSONETequipment,
10GBASE-ERisusedtosupport"darkfiber".
·10GBASE-LX4useswavelengthdivisionmultiplexingtechnologytosendsignalsatfourtimestheopticalwavelengthonasinglepairofopticalcables.Thesystemrunsunder1310nmmulti-modeorsingle-modedarkfibermode.Thedesigngoalofthissystemisforthemulti-modefibermodefrom2mto300morthesingle-modefibermodefrom2mto10km.
△Ethernetconnection
Futurenetworkdevelopmenttrend
